
Is Trintellix Good for Major Depression? Trintellix Pros and Cons
Photo from gettyimages
Originally Posted On: Pros and Cons of Using Trintellix to Treat Severe Depression (alternativetomeds.com)
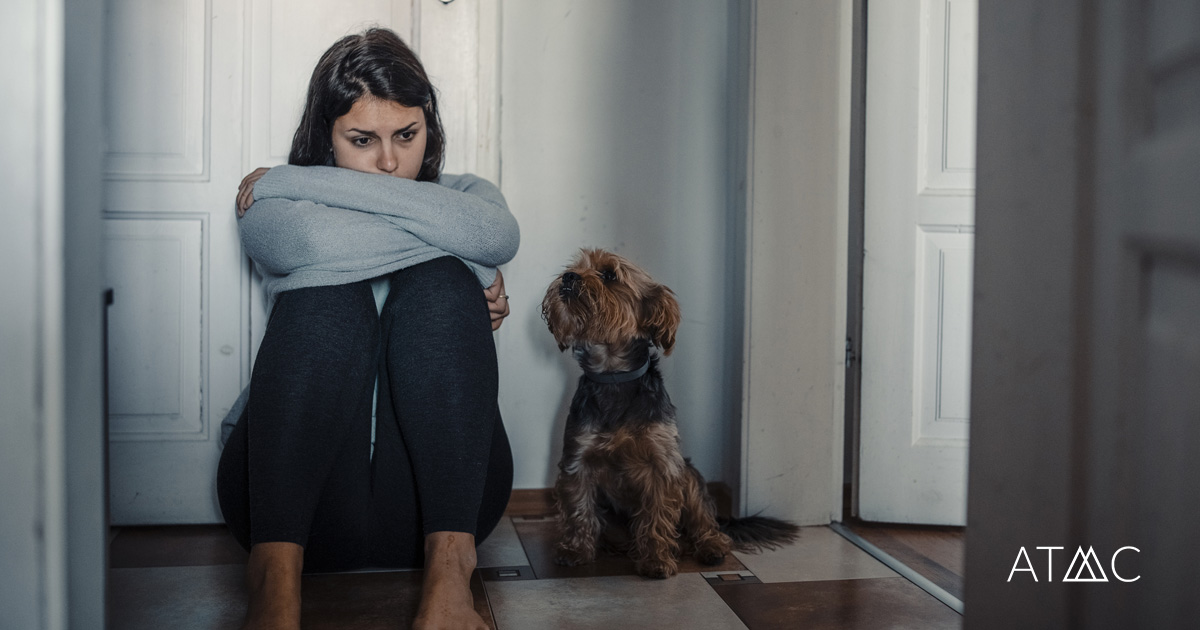
For most people, experiencing loneliness or sadness is a normal reaction to dealing with life struggles or losses. Unfortunately, sometimes those feelings fail to resolve themselves and become overwhelming. They may produce physical symptoms that interfere with handling daily activities and enjoying life. When these conditions persist for more than two weeks, you may be dealing with a common but serious mood disorder known as depression. Depression is a treatable mental health disorder. Mental health care providers often use a combination of therapy and medication to alleviate the symptoms of depression and help people develop the coping skills they need to enjoy life.
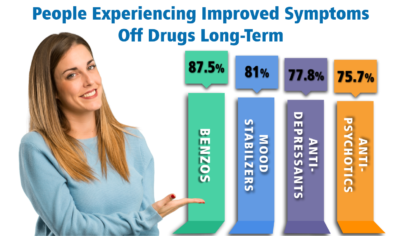
Alternative to Meds has more than 15 years of experience as an antidepressant withdrawal help authority. Using holistic therapies and Environmental Medicine, we have published evidence demonstrating the wonderful success of the majority of our clients in beating not only their dependence on medication but beating their depression symptoms as well.
What Is Depression?
Depression is one of the most prevalent mental health disorders in the United States. Ongoing research indicates that depression results from a combination of psychological, biological, environmental, and genetic factors. Depression can occur in people of any age but commonly occurs during adulthood.
Depression can be a response to a traumatic event, life change, or extreme stress. Sometimes medication prescribed for physical ailments causes the onset of depression. It can also co-occur with illnesses, such as diabetes, heart disease, cancer, or Parkinson’s disease. Having a family history of depression or other mental health disorders may also put you at higher risk for depression.
Major depressive disorder is more commonly known as clinical depression. It causes severe symptoms that impact how you think, feel, and your ability to handle your daily life. Major depressive disorder makes things like working, spending time with family and friends, eating, or sleeping feel almost impossible.
Symptoms of Depression
If you experience more than five of the following symptoms along with low-level mood and energy for more than two weeks, you may be suffering from major depression.
The number of symptoms and the severity of the issues will vary from person to person.
- Lack of energy and excessive fatigue
- Difficulty making decisions, inability to concentrate, or memory issues
- Ongoing feelings of worthlessness, helplessness, or guilt
- Extreme irritability or restlessness
- Feelings of hopelessness and overriding pessimism
- Changes in appetite, weight loss, or weight gain
- Changes in sleep habits—either sleeping too much or insomnia issues
- Persistent feelings of emptiness and sadness, or ongoing anxiety
- Loss of interest in pleasurable activities, including sex
- Unexplained headaches, cramps, aches and pains, or digestive issues that do not resolve themselves with treatment
- Increasing fixation on death, suicidal thoughts, or attempted suicide
Your doctor will ask when your symptoms began, how long you have been experiencing them, the severity of the symptoms, whether depression or other mental health issues run in your family, and if you have any history of drug or alcohol abuse. They will also likely ask if you have had prior bouts of depression, how long they lasted, and what type of treatment you used to address your depression.
Three Therapies for Depression
The earlier you begin treatment for depression, the more effective your outcome will be. Even in the most severe cases, there are medications and therapy treatments that can alleviate your symptoms. Depression is typically treated with psychotherapy, medications, or a combination of the two. Today, in addition to the typical psychotherapy-medication path, more emphasis is on behavioral therapies in conjunction with alternative medicine treatments and environmental therapy. The following are just a few of the treatments in use to alleviate symptoms associated with major depression.
1. Psychological Treatment
 Photo from gettyimages
Photo from gettyimages
Psychological treatments, also known as talk therapy, are a critical factor in successfully treating major depressive disorder. Psychological therapy focuses on teaching you strategies to better deal with negative thinking patterns, establish better coping skills, and process unresolved trauma. Various types of therapy fall under the umbrella of psychological treatment, and psychotherapy can be experienced in different formats. Depending on your needs, treatment may involve more than one format. Standard psychotherapy formats include individual therapy, group therapy, couples therapy, and family therapy.
There are several types of psychological treatments available.
The ones that have shown the most success in treating depression are:
- Cognitive therapy. This short-term goal-focused therapy concentrates on the ways our thought patterns impact our emotional states. Cognitive therapy helps you identify and change negative thinking patterns or cognitive distortions. Mindfulness-based cognitive group therapy uses mindfulness meditation practices to make you more aware of your thought patterns and help you focus on the present moment.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). This short-term therapy is one of the most effective psychological therapy options for treating depression. CBT effectiveness is based on the understanding that the way we think and act affects the way we feel. CBT focuses on identifying distorted thoughts or beliefs that cause negative feelings or actions. It does not consider unconscious issues from your past. Therapists work with you to identify the thought patterns and behaviors contributing to your depression, change negative or irrational thought patterns, and modify behaviors.
- Interpersonal therapy (IPT). This is also a more limited therapy addressing past and present interpersonal interactions to determine how interpersonal conflict and lack of social support impact depression. Therapy may look at conflict resolution techniques in relationships with family, partners, or coworkers.
- Psychoanalytic therapy. This type of psychological treatment is an internally focused treatment that works on the assumption that your current depressive disorder is connected to unconscious unresolved childhood issues. This long-term therapy can build self-awareness by helping you understand how feelings and emotions from the past contribute to your present-day situation.
2. Behavioral Treatment for Depression
 Photo from gettyimages
Photo from gettyimages
Behavioral therapy differs from cognitive therapy in that it focuses on changing behaviors rather than thought patterns. This type of therapy helps you identify and participate in activities that will enhance your positive feelings and overall well-being. Behavioral therapy enables you to identify unhealthy or self-destructive behaviors that may contribute to your depression and replace them with more positive ones.
A central component in behavior therapy is behavioral activation. When you are suffering from depression, you are more likely to avoid participating in activities you enjoy. This results in increasing isolation, higher anxiety levels, and a worsening of your mood, compounding your depression. Behavioral activation helps you identify specific pleasurable activities and set goals to incorporate them into your daily life. Learning this coping strategy can increase your chances of successfully reducing your depression symptoms.
The different types of behavior therapy include behavioral and cognitive play therapy, system desensitization, and aversion therapy, among others.
3. Environmental Treatment
 Photo from gettyimages
Photo from gettyimages
Environmental therapy treatment focuses on the impact that a patient’s physical environment has on their physical and mental health. Environmental factors can be your workplace environment, your home, food, air, or water. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control suggests many diseases may result from environmental or lifestyle factors. Environmental medicine is based on the belief that allergic and toxic substances produce subtle reactions in the body that accumulate over time, causing illness or disease and behavioral and mental disturbances. Practitioners focus on identifying and removing environmental issues that may cause illness and reducing exposure to toxins. The next step is detoxifying and cleansing the body of all toxic substances and integrating practices that support holistic recovery and healing.
Another form of environmental therapy, or eco-therapy, involves getting back to nature. Eco-therapy practitioners believe that modern society’s focus on technology and its alienation from nature cause much of our depression and anxiety. Since the Industrial Revolution began, our focus has become increasingly removed from the outdoors. The cure, eco-therapists think, is to get outside and enjoy nature. University of Essex researchers found that walking outside in nature every day can be as effective as antidepressant medication for mild-to-moderate depression.
Medications
Medications are often used in conjunction with therapy when therapy alone is not having the type of impact necessary. Antidepressants are the most commonly prescribed medicines for treating depression. Antidepressants attempt to correct chemical imbalances related to severe
cases of depression that don’t respond to therapy alone. You may have to try several antidepressants to find one that has manageable side effects and helps with your symptoms. Your medication may take two to six weeks before you see an impact on your symptoms, so be patient. Also, do not abruptly stop taking your medication. A doctor will need to help you safely decrease your dosage.
How Trintellix (Vortioxetine) Works to Treat Depression
One of the contributing factors in major depression is decreased levels of serotonin in the brain. Many doctors will prescribe antidepressant medication to address this imbalance. If your doctor recently prescribed Trintellix for your major depressive disorder, you likely have a few questions.
1. What Is Trintellix (Vortioxetine)?
Trintellix is a doctor-prescribed antipsychotic and antidepressant medication used in treating adult major depressive disorder. Trintellix targets the serotonin neurotransmitter.
2. What Type of Antidepressant Is Trintellix?
Trintellix is a multimodal antidepressant or an atypical antidepressant medication. Like many other antidepressant medications, Trintellix works by increasing serotonin levels in the brain by preventing serotonin reabsorption. However, unlike many SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) that only work by reuptake inhibition, Trintellix also works via the mechanism of serotonin receptor activity modulation.
3. Does Trintellix Help With Major Depressive Order?
Clinical research demonstrates Trintellix effectively reduces symptoms of depression. Research found at least 50 percent of patients prescribed the drug for their depression saw a 50% reduction in symptoms. Nearly a third of those in the study had almost complete or complete relief from symptoms. Trintellix showed improvement in several aspects of cognitive function associated with severe depression.
4. Is Trintellix a Mood Stabilizer?
Trintellix is not a mood stabilizer in the same category of drugs such as lithium. However, due to its dual modality, it is prescribed in some instances for those with a bipolar disorder diagnosis in conjunction with other treatments.
Trintellix: Pros and Cons
 Photo from gettyimages
Photo from gettyimages
If your health care provider has prescribed Trintellix to alleviate your severe depression symptoms, it is important to weigh the pros and cons of using this medication. Trintellix may be more effective in treating symptoms of depression than other antidepressants, and most people find it easier to tolerate.
Pros
- Trintellix has a similar rate of efficiency as other SSRIs in treating major depression.
- It has shown a lower risk of weight gain than other antidepressant medications.
- In comparison with other antidepressants, Trintellix has a reduced risk of sexual dysfunction.
- Trintellix has similar side effects compared with other SSRI antidepressants.
Cons
- Trintellix, like other antidepressants, poses a risk of increased suicidal thoughts in users under the age of 24.
- Trintellix users typically report higher rates of nausea than those taking other antidepressants.
- Using Trintellix combined with other medications or herbal supplements that increase serotonin levels can result in a dangerous condition known as serotonin syndrome. The condition includes fever, seizures, and muscle rigidity.
- Trintellix can increase your risk for bleeding issues or hyponatremia (low sodium).
- Using Trintellix or any antidepressant medication can cause a physical dependence on the medication.
Side-Effects of Using Trintellix to Treat Depression
Like any other medication, Trintellix comes with side effects.
The most common are:
- Decreased sex drive
- Heartburn
- Gas and constipation
- Dry mouth
- Blurred vision
- Spinning sensation
- Change in taste sensations
- Nausea and vomiting
More severe side effects that require a call to your doctor are:
- Coordination issues
- Agitation
- Muscle twitching
- Increased thirst
- Breathing issues
- Vomiting blood
- Seizures
- Black stools
Trintellix can cause many serious side effects, including serotonin syndrome, hypomania, increased bleeding, vision problems, discontinuation syndrome, and low salt levels. Be sure to keep up with your regular health care appointments.
What to Do If Your Antidepressant Stops Working
 Photo from gettyimages
Photo from gettyimages
There are several reasons your antidepressant no longer works, including smoking, alcohol use, drug interactions with a new medication, undiagnosed secondary conditions, changes in age or metabolism, or a built-up intolerance to the medication.
If you feel your antidepressant medication is no longer working, or you are unsatisfied with the side effects of your current medicines, talk to your doctor. It is important to have the proper support when changing medications or adjusting dosages. If your medication no longer works, there may be better alternatives. Contact Alternative to Meds for more information on treatments that can help with your depression.
1 (800) 301-3753 for Trintellix Tapering Help
Sources:
https://psychcentral.com/drugs/trintellix
https://www.verywellmind.com/what-to-do-if-your-antidepressant-has-stopped-working-1066864
https://us.trintellix.com/treatment/side-effects
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/depression/index.shtml
https://www.healthline.com/health/depression/cognitive-behavioral-therapy#an-experts-take
https://www.verywellmind.com/types-of-psychotherapy-for-depression-1067407
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430661/
https://save.health/mental-health/antidepressants
https://www.webmd.com/depression/news/20180222/antidepressants-do-work-some-better-than-others
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03598868
https://www.verywellmind.com/increasing-the-effectiveness-of-behavioral-activation-2797597
