BTU Explained
Photo from Unsplash
Originally Posted On: https://becoolachouston.com/btu-explained/
If you are shopping for or have ever shopped for an air conditioner or heater, you may come across the three-letter acronym BTU. If you never had BTU explained to you, or you are not an engineer, BTU’scan be a bit confusing to see it on cooling or heating home appliances.
But what is BTU, why is it important, and why do you need to know about it? To figure it out, you don’t have to be an engineer or a science whiz. We’ve provided all the answers to these questions!
What is BTU?
BTU is an acronym for British Thermal Unit, which refers to a measurement used to represent the energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water by 1 degree Fahrenheit. Even though BTU is commonly used in the UK, it is also used worldwide and is often used with energy, power, air conditioning, and steam production. BTU is the standard heat measurement in heaters, air conditioners, humidifiers, dehumidifiers, and radiators and should be featured in the device specifications.
BTU and the HVAC System
As we have learned, BTU is the amount of energy it takes to generate a specific amount of heat. The BTU rating shows how powerful the appliance is when it comes to HVAC systems such as heating and air conditioning devices. For instance, if your air conditioner or heater is labeled 12,000 BTU, it can generate 12,000 BTUs of energy every hour.
The higher the BTU rating of a heater, the more powerful it is, meaning it has a higher heat output than one with a low BTU rating. Therefore, it can quickly raise the temperature in your living space or heat a larger room more efficiently than one with a low BTU rating.
Because BTU is a heat-related energy measure, you may wonder how the BTU label fits on air conditioners. Air conditioners are designed to cool spaces by removing heat instead of bringing in cool air. An AC is equipped with a compressor that absorbs heat, draws it out of the room, and releases it outdoors. In this case, the BTU is not a measure of how much heat is added but how much energy the AC consumes to remove the heat using the compressor. So, remember that BTU is a measure of energy other than direct heat.
As with the heater, the higher the BTUs on an AC, the more efficiently it cools. The BTU rating of an AC can give you an idea of how powerful it is.
Which BTU Rating Do You Need?
When it comes to HVAC installation, BTU plays a critical role in choosing the right heat pump, cooling appliance, or heating appliance for your home. For instance, if you choose an AC with a low BTU rating to cool a large room, it will constantly run to cool the entire room. That way, you increase your electricity bill and still leave it hot.
When HVAC experts advise about sizing your air conditioning unit, they mean that you get an AC with the right cooling capacity (BTU) in relation to your space. The higher the BTU rating, the more powerful an AC unit is. However, don’t overspend on a higher BTU AC if you don’t have a big room; get one sized for your space.
What BTU rating do you require? The BTU count you need to cool your space mainly depends on the size of your room – how much air you need to cool. You can figure this out by measuring the length and width of your room and then multiplying the figures to get the square footage of your room.
With your room size in square footage, you can check the BTU chart and see the corresponding BTU rating. For instance, a small room of 150 square feet corresponds to 5,000 BTUs. However, a space two times as large does not require two times as many BTUs.
Below is a BTU chart that can give you a rough guide on BTU ratings based on square footage:
Room Square Footage Corresponding BTUs
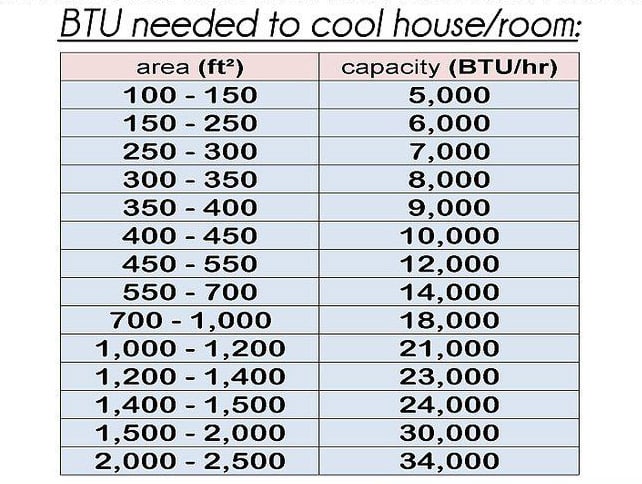
There is more to choosing the right heater or air conditioner BTU rating for your room. Indeed, the rule of thumb is to get the square footage and check your BTU chart of appliance specs. However, consider the following factors when choosing your BTU for a heater or air conditioner.
- Ceiling Height: when sizing your AC unit, it is the total volume of air you intend to cool and not the floor area of your room. So, when BTU recommendations are provided, they assume standard 8-foot ceilings. But if you have a higher ceiling, there would be increased air volume, thus requiring a higher BTU rating.
- Unit Location: An AC unit installed in direct sunlight will work harder to cool, so consider adding at least 10% to your BTUs for ac units to be installed in natural sunlight locations.
- Insulation: if you have a well-insulated home, consider a lower BTU unit than a home with low or average insulation. For poorly insulated houses, consider a higher BTU rating.
- The shape of a House: A house with a compact shape requires less energy to cool, while a ranch house with multiple wings usually has more cool air to dissipate. In a nutshell, the more expansive the home is, the more BTUs are required to keep it cool.
However, if you have a room with a high ceiling, multiple windows, or poor insulation, consider a heater or air conditioner with the highest BTU rating recommended for your room size, or choose the next BTU rating to be on the safe side. This recommendation works better for space heaters, portable ACs, and window units. But for whole-house HVAC installation, consult an expert HVAC technician for guidance.
